POS System Software: From A to Z
Updated: Dec 7, 2021

Following the last Grand View Research, Inc. forecast, the global POS market value will grow up to USD 125.9 billion by 2027, with a 7.5% CAGR. What else can be strong evidence that the software for POS systems matters a lot for most industries? Earlier, JEVERA highlighted small parts of this issue, but it’s time to see the bigger picture. Let’s consider everything that a retailer, restaurant/hotel manager, or gas station chain owner should know about a Point of Sale system.
How Does The Point of Sale Software Work: Basic Principles
There are so many definitions of what a POS system is as many companies that have it. For each user, Point of Sale performs customized functions. That's why there are significant distinctions in its understanding.
In general, Point of Sale is a set of hardware and software that forms a place of transactions conducting. Here this is the main feature, as well as transferring information to state authorities for tax purposes. The above qualities are similar for every type of Point of Sale in any field. In rest, everything depends on the user's needs and business condition. Among the principal tasks, the POS system can provide the following:
inventory management;
internal reporting;
generating of customer information;
logistics management;
loyalty system support, etc.
Point of Sale has two types of equipment:
hardware purchased from the companies, certified by fiscal authority (like a recorder);
other equipment, which users can buy from any sellers (cashier screen, keyboard, etc.).
The first one provides permanent and accurate tax data transferring. The manufacturer and distributor of such equipment have a special audit first and then get a license or other authorization document allowing them to produce/sell hardware. They are fully liable to a state for any errors in its operating.
Requirements for the second group are less harsh. All other equipment should perform its functions well and seamlessly interact with leftover system elements.
Thus, the software for Point of Sale system serves the transactions, reporting about a new operation to the fiscal authority in real-time through the recorder. A client gets only a check or invoice, unaware of how many processes the POS can do at this moment. For instance, to change the data in reports, gather updated information about his customer experience, and so on.
A great variety of domains needs a Point of Sale system. Amount them Retail, HoReCa and Hospitality industries, Gas stations, Consumer services (like car washing or spa). In Canada, there are even POS systems for cannabis sales. They allow determining the buyer and staff's age, correctly generate tax reports, and create detailed automatically updated customer profiles.
As seen, each of these businesses has an original POS far from the usual idea of it.
How Many Different Types of POS Systems Are There?
Point of Sale systems differs not only in functionality but also in the type of:
equipment,
development,
data storage,
portability, etc.
It's advisable to combine the POS classification by functionality and usage areas, as the first condition directly depends on the last one. Thus, in this case, the systems are divided into Retail, Hospitality, HoReCa, Gas station, etc. It should be noticed that even within one industry, Point of Sale can perform completely different tasks (for example, in grocery and non-grocery stores, or a restaurant and a small bar).
By type of equipment, systems are divided into ordinary and touch screens. An example of a traditional system is the cashier's workplace hardware in a supermarket: a regular desktop and a barcode scanner, a screen for the customer, and other additional equipment. Here the employee enters data using the keyboard.
Touch screen POS system software requires a touch screen hardware base (like those that people usually see near the McDonalds cashier place) and additional devices (tablets) supporting this feature. This type of POS is used in restaurants. It helps to take orders quickly and unmistakably.
By the type of development, POS systems could be vendor and custom. Both of them are designed by vendors (suppliers). But the vendor system is a universal solution for industry (like the hotel business). Here developers cannot consider every user's conditions. They create a digital product that can cover the joint weaknesses of this area. Such POS are subscription-based. They usually have a high scalability level because of proceeding with countless amounts of data from different companies. Solutions provide a relatively low subscription cost and core process support needed by small and medium-sized businesses.
Custom POS systems are the complete opposite of vendor ones. They are developed specifically for one customer company, taking into account all its needs. The development cycle is time and money consuming, but the customized result is worth the effort. Here POS systems might be hybrid and perform varied functions.
There are also vendor lock-in and Open API POS. In the first case, users cannot change the components of the solution whenever it's needed. The customer itself can improve the open API Point of Sale.
By the type of data storage, Points of Sale are divided into on-premise, cloud, and hybrid. The first one works on the ordinary desktop principle. It provides data access via using the equipment directly connected to the server. In this case, the server is located at the place of business activity. The second kind of system uses Cloud technologies. They allow access to data from any device connected to the internet. The hybrid type combines the features of the previous two, partially storing data on the local server and the cloud.
There are two types of portable Points of Sale: mobile systems and POS applications. Following Statista, the transaction value of mobile POS payments will grow up to over US 4 mln 2024 (CAGR 19.2%). It means that such a solution becomes more popular, especially in coronavirus conditions. This system requires special additional equipment to function. Meanwhile, a compatible mobile device is sufficient to use a Point of Sale app. Both products allow conducting transactions from any place.

Retail POS System Software Features
POS systems in the retail industry vary significantly depending on what the retailer is selling. It's worth looking at Point of Sale through the prism of grocery retail. Here everything is simple. The POS system is considered as a cashier's workplace, performing its main functions:
conducting of transactions,
transfer tax data to the fiscal authority.
For grocery retail, the speed of service is principal. Here the POS works to provide it. Many stores use self-checkout counters to reduce queues and minimize communication with staff.
The system also supports loyalty programs, but as an additional interface for displaying data. POS systems should integrate well with equipment in the hall and create a kind of AI ecosystem. A simple example of such integration would be the fridge's automatic opening with Pepsi after payment for the desired drink.
The food retail POS system has to support the "click and collect" option. Today it's necessary to provide customers with the opportunity to quickly receive a purchase, avoiding crowds of people inside brick-and-mortar stores.
Besides, retailers cannot reach success without using a customized approach. The Point of Sale system can support it by automatically updating the details of each customer profile. Thus, here the main areas of POS development should be:
the provision of fast and contactless food shopping;
improving the level of integration with the marketing department software.
Grocery's POS capabilities can significantly improve the customer experience, personalize the offer, and increase the customer's Lifetime Value (LTV).

POS for electronics stores, for instance, performs many more functions than a grocery one. It can rightfully be called a store management point since the range of tasks is much outspread than at a regular Point of Sale. These retailers don't care about customer service speed. They focus on software multifunctionality.
Here the Point of Sale has the following features and functions:
High level of workflow. It includes not only receipts and invoices but also warranty coupons and other documents.
Management of goods. For example, checking the product availability, forwarding them from one store to another, booking, etc. For this purpose, clothing stores often use portable handheld devices with a built-in barcode scanner.
Pricing management. Electronic price tags are used as additional equipment to change prices faster and accurately.
Controlling equipment inside the sales area, such as audio advertisements playback installations, etc.
Nevertheless, despite its versatility, the POS system in non-food retail is also weakly connected with the marketing department. A high degree of interaction between Point of Sale and marketers will allow a company to receive much more data on customer behavior trends and meet demand on time based on precise forecasts.
Pharmacy POS System: Ordinary Software Or Digital Pharmacist
Pharmacy Point of Sale software is so similar to the retail one, except for the lack of electronic scales and the ability to manage various processes (as non-grocery stores' POS can). Nevertheless, these systems still have peculiarities. First, behind the pharmacy counter, a pharmacist - a person with specialized education will serve you. He/she can advise which product is appropriate for a particular disease. Most often, clients do not come for a specific drug but with a specific problem: for example, a sore throat. A pharmacist can suggest effective medications based on symptoms. Here the POS system's task is to ensure the drug search analyzing existing stocks.
However, pharmacy Point of Sale systems often move beyond these boundaries, becoming smart assistants to the pharmacist. It is enough to indicate symptoms, and a Point of Sale will obtain a set of medicines applicable in each specific case. Moreover, in this case, the system can issue additional prompts, for example, to clarify whether the customer is allergic to a certain drug's component.

As with retailers, service provision speed also matters to this industry. Since most customers don't know what exactly they want to buy, speed lack is a huge issue.
One minute of a client's waiting is equal to a negative customer experience and significant losses. Smart POS can prevent it by optimizing pharmacist performance and increasing throughput.
In addition, to form a pharmacist's workplace and analyzing medical inventory, POS systems for pharmacies can:
provide transactions and communication with tax authorities;
track the drugs' expiration dates;
verify the authenticity of prescriptions, integrating with state healthcare system;
authorities databases;
maintain a high level of upsells by providing on-time notifications about existing discounts through integration with the loyalty system;
generate reports;
confirm online purchase requests;
integrate with equipment inside the pharmacy (refrigerators, a ventilation system, and closed shelves).
Many pharmacies practice installing smart mobile Point of Sale devices throughout the sales area. They help buyers to choose products, form an order, and pay for them at the checkout. In coronavirus conditions, this approach is a safe alternative to long-term communication with pharmacists.

Following the latest G2 ranking, the best ready-made pharmacy POS systems are Computer-Rx, CashierLive Pharmacy POS, Anvesha Pharma, etc.
Point of Sale Systems For Restaurants, Hotels, And Bars
Restaurants also need robust, multifunctional Point of Sale due to the variety of processes that the system must control. Here POS performs the following functions:
Product recording. It helps to understand how many products are used and for what purpose, and how many products need to be purchased in the future.
Menu management. To achieve the above goal, employees enter menu items into the system that stipulate how many ingredients of what weight should be used for dishes.
Staff management. Restaurant POS system software helps to schedule the work of all personnel and monitor its implementation. So the manager always knows who is on shift on a particular day.
Hall management. The information about the tables and also the waiters, who are assigned to them, is entered into the system. This function enables to understand which tables are available and which are not; perform a table reserve function; track the occupancy statistics.
Order management. The system allows tracking the correctness of order, transmitting information directly to the kitchen in real-time. The waiter doesn't have to waste time telling the chefs which dish is next in line. They see this information on their devices immediately after the checkout.
Thus, in restaurants, a Point of Sale doesn't live up to its name either. It becomes the point of management, running almost all the functions. The speed of service is highly crucial for this business, so managers choose touch screens, cloud POS. It enables taking orders as quickly and accurately as possible. Since the information is accessible from any device, it's convenient for all cashiers, waiters, and kitchen workers to use it.
Point of Sale software for bars is much simpler. Since they rarely form chains, the POS system is sufficient to cover the following issues:
accounting for alcoholic beverages usage;
formation of tax reporting;
less commonly, hall management in the context of table reservation and hall occupancy control.
Thus, the bar owner needs a simple and inexpensive solution that can fulfill the above functions. The function of staff management is almost always absent due to the small number of bar employees.

The hotel's Point of Sale system is also complex and multifunctional. The most significant need for this business is the maintenance of the rooms themselves or the assets management. It's the primary function that POS should perform here. It provides the ability to control the:
hotel occupancy level,
booking (for it POS must also integrate with any external services, such as Booking.com, AirB&B, etc.),
cleaning,
frequency of repairs.
The system also performs the following functions:
keeping records of the water and electricity usage;
personnel management;
interaction with a hospitality industry (mostly for resort hotels);
integration with other hotel services systems: restaurant, spa, beauty salon, etc.
So, it should be a complex and reliable system that processes large amounts of data but allows the guest to feel the purchase of all services as one directly related to accommodation.
Why POS System For Gas Station Is A Base of Its Functioning
POS system for gas station is a mechanism that unites almost all equipment at a point into a single AI ecosystem. Businesses rely heavily on this software. That's why here it performs the following functions:
gasoline supply control (including ordering, acceptance, and filling of containers);
accounting for fuel usage;
excisable goods sale management (since gasoline is subject to excise tax);
formation of complex financial statements;
staff management;
refueling control;
running the sale of food and non-food products (every purchased bar of chocolate or toy revealed in the gas station accounting records).
As seen, POS systems have a high level of integration with additional equipment. They allow to fill the tank, make coffee, and take sandwiches from the fridge without assistance. This system must support the restaurant function if there is one on the station territory. It means that the POS must perform all the functions inherent in the restaurant Point of Sale.
The cost of personnel error at a gas station is so high, as it requires complete financial statements change. Thus, the perfect POS system, in this case, should minimize the employees' impact. It will reduce the level of mistakes in service Мprovision.
Thus, in the field of gas stations, the Point of Sale software is complicated and covers almost all processes occurring on filling points.
Box Solutions & Custom Made POS Systems
Following the above, the main difference between box or vendor and custom POS solutions is the target audience.
Vendor solutions are universal. Supplier designs them on their initiative, analyzing a specific business area as a whole. Here POS software providers a convenient usage for companies that need a general coverage of their simple business processes. Bars and small cafes often choose vendor solutions because they have an affordable price and regulate all the procedures required by these enterprises. Vendor solutions from such market giants as Microsoft, SAP, and Oracle are distinguished by high reliability. They ensure complete data safety and smooth system operation.
Thus, the main benefits of vendor POS systems are:
Relatively low price.
Reliability.
High level of scalability. It processes significant amounts of data.
Operation on the subscription base excludes long-term business relations with the vendor and increases user flexibility in choice.
But these systems have several disadvantages, including:
The general approach. Developers cannot analyze the needs of each potential client and adjust the software for it.
Dependence on the supplier. The user doesn't have the opportunity to change the product components following its needs. It has to wait for a new POS version from the vendor, which does not always solve the problem.
Box Point of Sale system is usually cloud-based. They can be mobile or provided as POS applications. Touch screen vendor solutions are also shared. This type of Point of Sale is used by small and medium businesses, including the above bars, cafes, restaurants, street sellers, and artisans. Other business areas can also use vendor POS if it fully covers the needs.
Custom development results are always personalized. The vendor develops a POS system for a specific customer who will use it. This procedure consists of 4 main stages:
Current situation analysis. It helps to understand what kind of solution the customer needs and what exactly it should include.
Preparation of the project plan. The development team creates a step-by-step map of how the design process will proceed.
Product development.
Delivery and deployment. This stage also includes final customer testing and transfer of intellectual property rights to the development result.
A custom Point of Sale can be developed by a contractor or an internal IT-team that will further support this product. The main advantages of custom Point of Sale are:
Personalized approach. Since the development is carried out for one company, the result will fully meet its requirements and needs.
Multifunctionality. Such a POS can contain different components inherent in other types of systems and perform a large number of complex tasks.
Flexibility. It's possible to change software components whenever a business requires it.
However, a custom POS system has significant drawbacks, due to which not every business wants to buy it. Among them:
The high cost of software development and support.
Time-consuming procedure. Following Goodfirms' research, the development project takes 4.5 months on average. This period might be longer and depends on the designed product complexity.
Partial vendor dependency. It refers to custom products developed by a contractor company. Each product change will occur at the client's request, while accompanied by the preparation of legal documents and the formation of the contractor's work schedule. Such issues do not arise when an internal IT-team develops the product.
Custom and out of the box software solutions are usually purchased by companies that require a multifunctional complicated POS system. Vendor products are unable to meet their needs. Thus, the custom Point of Sale is used in large chain stores such as Walmart, Costco; restaurants; hotels, like Hyatt, Hilton, etc.
By the way, almost all gas stations use custom development results because of the large number of tasks that POS will have to perform
Following the above, custom Point of Sale can be completely different: traditional or cloud-based, using conventional or touch screen hardware. It all depends on the client's wishes and needs.
Legacy And Cloud-Based POS: Main Distinctions
Remember that these two types of POS save data in different ways. Legacy POS systems work based on a local server. All information is stored on it and has limited access from devices directly connected to the server. Usually, system components are updated on-site in a manual manner. The development team comes to the server location and makes the necessary changes.
Cloud POS system stores all data on remote servers, allowing access to them from any device anywhere in the world. All changes to the system components performed remotely, which does not affect the subscriber work, which smoothly switches to using the new POS version.
There is also a third type of Point of Sale. It combines the advantages of both approaches. Here the part of the data is stored on the server and the other on the cloud. Vendors developed a large number of such solutions. They remain the most demanded by businesses. The shining example of such software products might be Revel, TouchBistro, EPOS.
Cloud-Based vs. Server-Based POS System: Which One Will Win?
Following the Hospitality Technology data, 61% of merchants want to have POS in the Cloud. It explains by noteworthy pros that the usage of these Points of Sale can give. For instance:
Permanent data access.
Reliability and scalability. They are capable of storing more data without loss or distortion. The information is also highly protected.
Frequent updates. Remote developers' work allows the enterprise to continue working and doesn't interfere with business activities. Therefore, the POS system updating is held once every several months.
A small amount of equipment. It's limited only to devices for gaining access.
Information transfer in real-time.
Nevertheless, Point of Sale software supporting cloud technologies has its drawbacks, including:
Network and coverage dependency. If the connection is interrupted, the work will be terminated until the signal recovery. Thus, on the roadside, such a system will work intermittently.
Data protection level. Yes, it's high, especially if a company buys Cloud POS systems from well-known vendors. But information access can lead to fraud or data theft.
HoReCa industry prefers to purchase Cloud Points of Sale. They transmit information in real-time, which means they allow quick service provision. It improves the customer experience. Besides, such systems are easy to use with staff. On the contrary, such a system is unsuitable, for example, for large retailers who need to conduct transactions under any conditions.
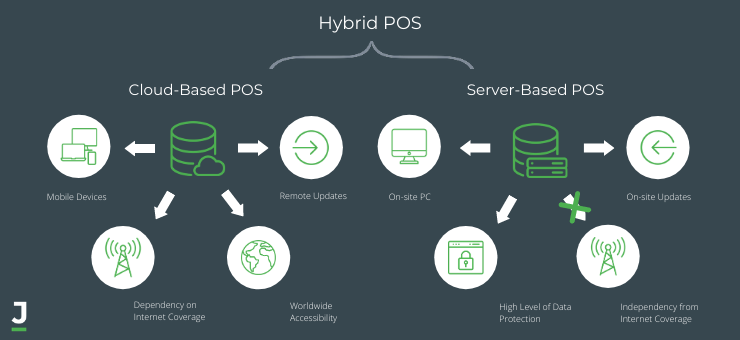
Despite traditional technologies, the On-premise Point of Sales also has advantages that allow it to stay afloat to this day. For instance:
Data security. Limited access and bulky equipment prevent information theft.
Uninterrupted system operation. This POS is independent of coverage and even electricity, as it can continue to work without both components.
Among the disadvantages of legacy POS software are the following:
Sparse component updates. They happen 1-2 times a year due to on-site made changes. The developers' work interferes with business activities. Thus, the inconvenience leads to a low level of system adaptability.
A large amount of equipment. It becomes a problem if the business space is small.
Gas station business area uses traditional POS Systems. This type of activity requires complete independence from the network connection and, for example, loss of power. The stations are located in different regions, where some problems with communication and electricity might arise. However, the system should continue to run smoothly. This industry also prefers the traditional approach due to the high degree of data protection. Reports of excisable goods sales must be kept safe. Despite the great desire, following Mordor Intelligence, 95% of brick-and-mortar stores process payments that take place with fixed POS solutions. Retail still uses traditional solutions to remain independent of external circumstances.
The Bottom Line
Thus, the Point of Sale systems market is quite diverse. Many available solutions suit any business. However, choosing the right POS is quite a complicated issue. Therefore, before a Point of Sale purchase, managers should pay attention to the current business condition, future development plans, material capabilities, and the acceptable time frame for product implementation. These components will help speed up the decision-making and buy a solution that will cover its weaknesses and support strong sides.



